Nerve Cell

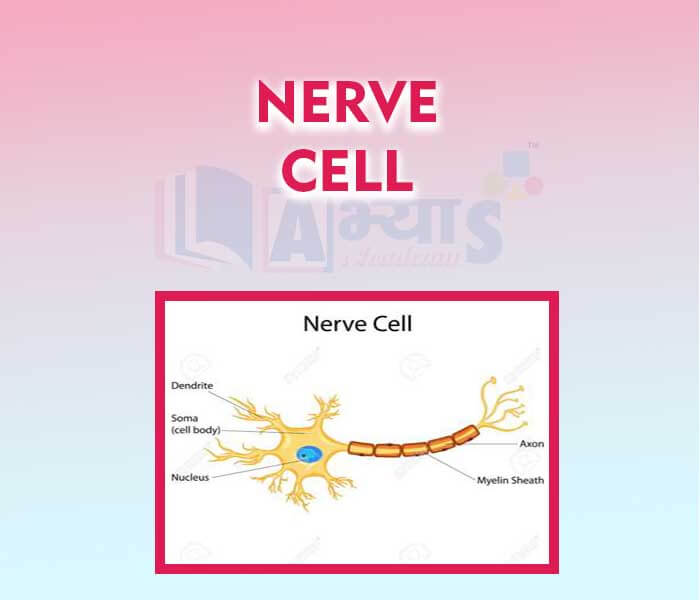
Nerve Cell
Control and coordination in animals depend on two things for information transmission - chemical signals of hormones and nerve impulses (electrical impulses). If they depended only on electrical impulses through nerve cells, a limited range of tissues would be stimulated. Since they get chemical signals in addition to the nerve impulses, a large range of tissues are stimulated. As a result, animals can show wide-ranging changes in response to stimuli.
Impulse: It is an electrical disturbance received by the dendrite and passed through the cyton to the axon. Messages are transmitted in the form of electrical impulses along the fibres of the neurons.It flows only unidirectionally.
Neurons: A neuron is the functional and structural unit of kidney.It consists of following parts:
Dendrites or dendrons: These are hairlike processes connected to the cyton. They receive stimulus, which may be physical, chemical, mechanical or electrical, and pass it on to the cyton.
Cyton or Cell body : It's shape may vary from round to stellate . It has large central nucleus surrounded by neuroplasm. Beside other cell organelles cyton contains Nissl's granules.
Axon: From one side of the cyton arises a cylindrical process filled with cytoplasm. This process is called axon. It is the longest part of the neuron. It transmits impulse away from the cyton. Its tip has a swelling called axon bulb. Generally, a neuron has one axon .Axon is covered with a sheath,made up of schwann cells,called neurilemma. In addition a neuron may be covered with myelinated sheath , such fibres are known as myelinted sheath fibres and those without this sheath are termed as non-myelinated sheath fibres. The ending of an axon may be branched. These endings are called synaptic terminals.
The gap between a synaptic terminal and the dendrite of another neuron or an effector cell is called a synapse. The neurons are not connected. There is minute gap called Synaptic cleft. With in axon there are synaptic vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotansmitters. The impulse that reaches the ends of the axon fibres causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter reaches the dendrites of the other neuron. This, sets up a new impulse which is transmitted to the axon. The speed of transmission is 120 m/s.
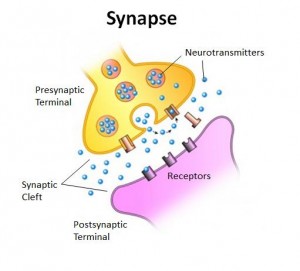
Myelinated nerve fibres conduct impulses more efficiently than non-myelinated nerve fibres. The myelinated nerve fibres possess unmyelinated areas at intervals called nodes of Ranvier.
Table : Differences between Dendrites and Axons
| S. No | Dendrites | Axons |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | These are short and tapering processess | These are long, uniform and cylindrical processess |
| 2. | A number of dendrites arise from the cyton | Only single axon arises per cyton |
| 3. | They have tapering ends | Terminal branches of the axon enlarge to form a knob |
| 4. | They contain NissI's granules and neurofibrils | They do no contain NissI's granules but contain neurofibrils |
| 5. | They receive sensation and send it to the cyton | They carry impulses away from the cyton |
A number of nerve fibres are wrapped together to form nerves. The nerves lie end to end in a chain so that the dendrites receive impulse, from an axon or receptor, passes it to the next neuron in the chain via its cyton and axon. The junction between the axon and dendron of the next neuron is called Synapse. It is the point of contact between the terminal branches of the axon of a neuron with dendrites of another neuron. The neurons are not connected. There is a minute gap called Synaptic cleft. Within the axons are synaptic vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. Transmission of nerve impulse is a chemical process. The impulse that reaches the ends of the axon fibres causes the synaptic vesicles to release the neurotransmitters (acetylcholine) into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters reach the dendrites of the next neuron. This sets up a new impulse which is transmitted to the axon. The speed of transmission is about 120 m/s. The chemical is soon broken down by an enzyme to make the synapse ready for the next transmission.
Which part of nerve cell contains nucleus? | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation |
The gap between two neurons is called a ________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The region where the nerve endings of one neuron come into contact with another neuron is called as ______________ | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
Abhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
