Alternating Current






Alternating Current
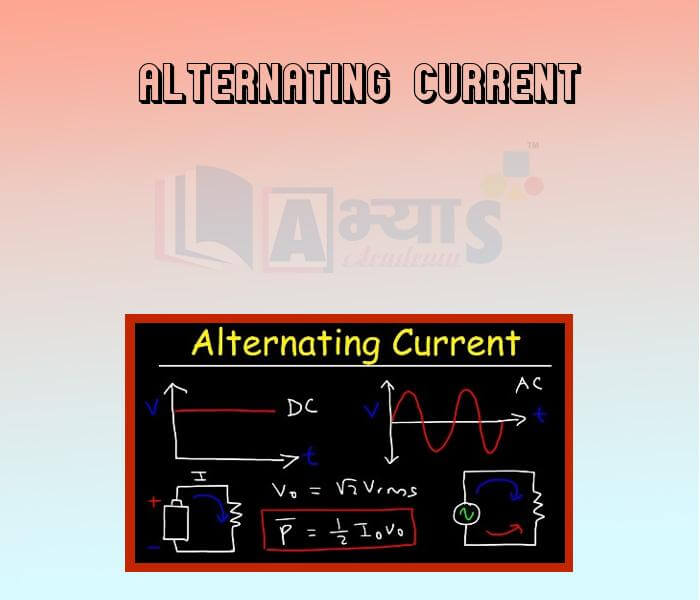
Direct Current (DC) : An electric current whose magnitude is either constant or variable but the direction of flow in a conductor remains the same is called direct current. It is denoted by DC. Sources of DC are voltaic cell, a dry cell, battery, DC generator, etc.
Alternating Current (AC): An electric current whose magnitude changes with time -and direction reverses periodically is called alternating current. It is denoted by AC.
Sources of AC are hydro-electric generators, thermal power generators and nuclear power generators, etc.
Suppose you connect a bulb to an AC source such as the AC supply of your house (Figure 5.23a),
.jpg)
The potential difference VA - VB across the bulb keeps changing with time. When the current flows from A to B in the bulb, VA > VB . When the current flows from B to A in the bulb, VA < VB. When the current becomes momentarily zero before changing direction, VA = VB.
In fact, the potential difference across the bulb changes gradually from a maximum value Vo, to zero and then to the minimum value -Vo From -Vo it increases to zero before reaching Vo. once again. The way the potential difference (voltage) across the bulb changes with time is shown in figure.
.jpg)
A plot of the alternating current through the bulb will also be similar. The number of cycles completed by the AC in one second is called the frequency of AC. Starting from a particular value (say, maximum or minimum), when the current or voltage reaches the same value next time, it is said to complete one cycle. If it completes 1 cycle in one second, we say that its frequency is 1 hertz (Hz). The frequency of our household AC supply is 50 Hz, i.e., there are 50 cycles per second, which means that AC changes its polarity after every 100th part of a second as it changes its polarity twice in one cycle. or we can say it changes direction 100 times in 1 second.
The major difference between AC and DC is that DC always flows in one direction, while AC reverses its direction periodically. The advantage of AC over DC is that electric power can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
When the current or voltage reaches the same value next time, it is said to complete _____________ | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
If the current completes 1 cycle in one second, we say that its frequency is _____________ | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
When AC current flow it becomes momentarily _______________ before changing direction | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
