Plasmolysis












Plasmolysis
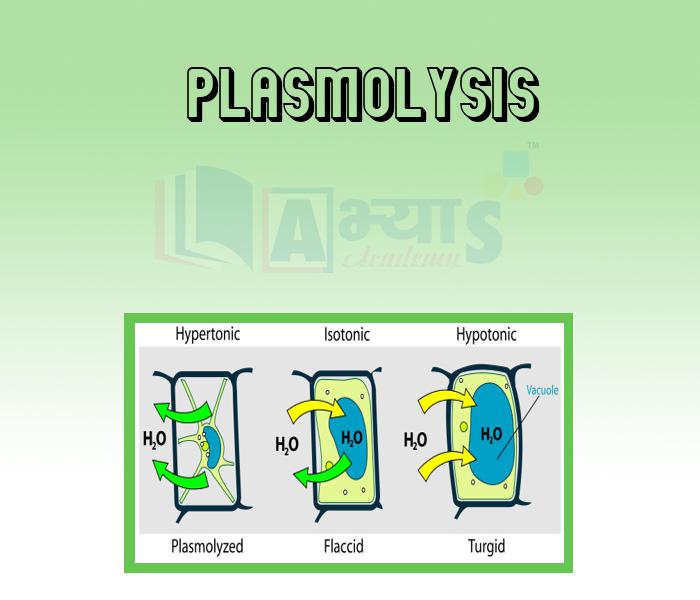
The plasmolysis is the condition which occurs when water tends to move out of the cells and the cell membrane of a plant cell shrinks away from its cells wall when it is placed in a hypertonic solution (having more concentration). During this process, the hypertonic solution causes exomosis (outward movement of water) and the water first moves out from the cytoplasm and then from the central vacoule. This withdrawal of water through diffusion into the extracellular fluid causes the cell to shrink in size, due to which cell moves away from the walls and the space thus, formed between the cell wall and the shrunken protoplast is occupied or filled by the external solution.
Limiting plasmolysis is the first stage of plasmolysis in which the pressure on the wall becomes reduced and gets contract cousing reduction in the cell size.
At limiting plasmolysis the pressure potential is zero and the pressure of external solution balances the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. Thus, during this state of equilibrium when flow of water into and out of the cell is same, the cells are called flaccid.
Deplasmolysis : - The process in which the plasmolysed cell when placed in pure water or hypotonic solutiom, builds up a turgor pressure (in which water enters the cell and cause the cytoplasm to build up a pressure against the wall). It is mainly responsible for enlargement and extensive growth of the cells.
Students / Parents Reviews [20]
Abhyas is good institution and a innovative institute also. It is a good platform of beginners.Due to Abhyas,he has got knoweledge about reasoning and confidence.My son has improved his vocabulary because of Abhyas.Teacher have very friendly atmosphere also.

Manish Kumar
10thIn terms of methodology I want to say that institute provides expert guidence and results oriented monitering supplements by requsite study material along with regular tests which help the students to improve their education skills.The techniques of providing education helps the students to asses...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thWe started with lot of hope that Abhyas will help in better understnding of complex topics of highers classes. we are not disappointed with the progress our child has made after attending Abhyas. Though need to mention that we expected a lot more. On a scale of 1-10, we would give may be 7.

Manya
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience with Abhyas Academy has been very good. When I was not in Abhyas whenever teacher ask questions I could not speak it confidently but when I came in Abhyas, my speaking skills developed and now I am the first one to give the answer of teachers question.

Upmanyu Sharma
7thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala cantt.The institute provides good and quality education to the students.The teachers are well experienced and are very helpful in solving the problems. The major advantages of the institute is extra classes for weak...

Shreya Shrivastava
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thUsually we see institutes offering objective based learning which usually causes a lag behind in subjective examinations which is the pattern followed by schools. I think it is really a work of planning to make us students grab the advantages of modes of examination, Objective Subjective and Onli...

Anika Saxena
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thThe experience was nice. I studied here for three years and saw a tremendous change in myself. I started liking subjects like English and SST which earlier I ran from. Extra knowledge gave me confidence to overcome competitive exams. One of the best institutes for secondary education.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas academy is great place to learn. I have learnt a lot here they have finished my fear of not answering.It has created a habit of self studying in me.The teachers here are very supportive and helpful. Earlier my maths and science was good but now it has been much better than before.

Barkha Arora
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
