Haemodialysis and Dialysis








Haemodialysis and Dialysis
Kidney failure and the Survival Kit - Haemodialysis: The kidneys may be damaged due to infection, injury, diabetes, and extremes of blood pressure. A damaged kidney cannot function efficiently to remove urea, ions, water, etc., from the blood. This malfunctioning results in the accumulation of toxic wastes like urea (uraemia), which can lead to death. One of the ways to treat kidney failure is to use a ‘dialysis machine’ that acts as an artificial kidney. Second way is to get your kidney transplant.
Procedure :
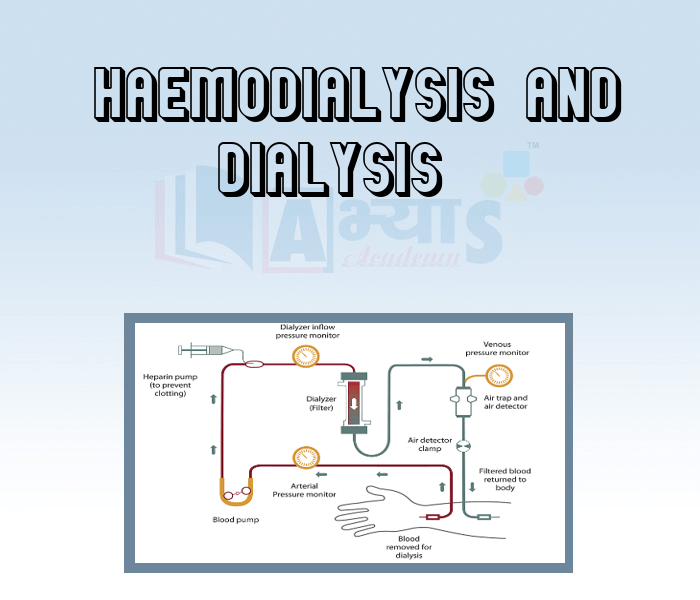
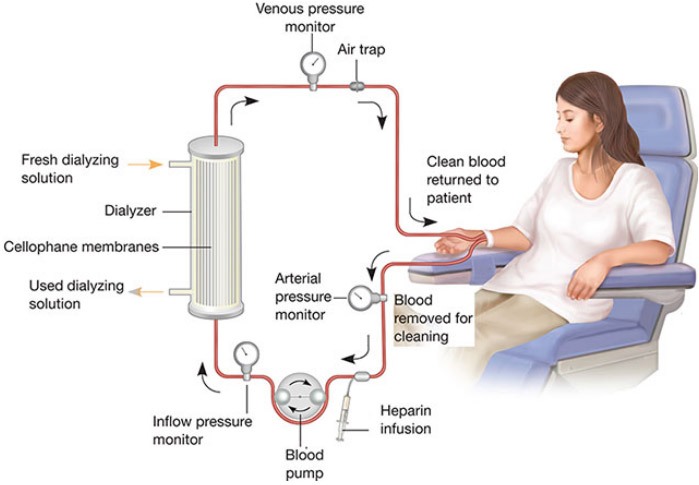
It has a long tubelike structure made of Cellophane suspended in a tank (dialyser) of a fresh dialysis fluid (dialysate). The Cellophane tube is partially permeable and therefore allows solutes to diffuse through. During dialysis, the blood of the patient is withdrawn from an artery and cooled at 0°C. It is maintained in a liquid state by adding an anticoagulant and by other special treatments. It is pumped through the dialysis machine. Here, the nitrogenous waste products from the blood diffuse into the dialysis fluid. The purified blood is then warmed to the body temperature and pumped back into the patient’s body through a vein.
The dialyser is specific for each patient to avoid infections. Dialysis through an artificial kidney has to be carried out at frequent intervals. This process of purification of blood is called haemodialysis.
A dialysis machine works like a kidney except that no selective reabsorption takes place in the former. An artificial kidney:
Haemodialysis
During dialyses the artificial kidney maintains the balance of ___________ and __________________ salts in a patient whose kidneys have failed. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
How often must hemodialysis usually be done? | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) The kidneys may be damaged due to infection, injury, diabetes, and extremes of blood pressure. (b) A damaged kidney cannot function efficiently to remove urea, ions, water, etc., from the blood. (c) The dialysis machine has a long tube like structure made of Cellophne suspended in a tank (dialyser) of a fresh dialysis fluid (dialysate) . | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.
