Rural Local Government
Rural Local Government
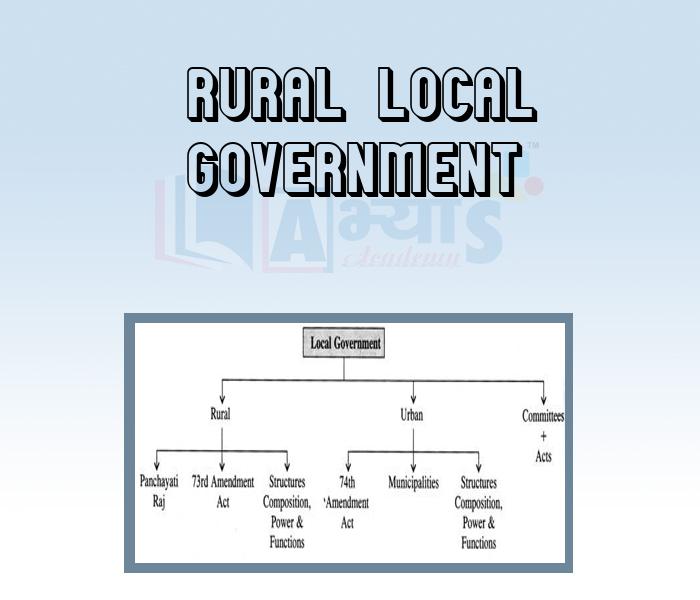
Rural Local Government: Panchayats or Panehayati Raj is a system of governance in which gram panchayats are the basic units of administration. It has three levels: village, block and district. Mahatma Gandhi advocated Panchayati Raj, a decentralised form of Govemment where each village is responsible for its own affairs, as the foundation of India's political system. His term for such a vision was "Gram Swaraj" (Village Self - governance).
Panchayati Raj system was adopted by state governments during the 1950s and bos as laws were passed to establish Panchayats in various states. It also found backing in the Indian Constitution, with the 73 amendment in 1992 to accommodate the idea. The Amendment Act of 1992 contains provision for devolution of powers and resporaibilities to the panchayats to both for preparation of plans for economic development and social justice and for implementation in relation to twenty-nine subjects listed in the eleventh schedule of the Constitution.
The panchayats receive funds from three sources
(1) local body grants, as recommended by the Central Finance Commission,
(2) funds for implementation of centrally-sponsored schemes, and
(3) funds released by the state governments on the reccmmendations of the State Finance Commissions.
In the history of Panchayati Raj in India, on 24h April 1993, the Constitutional (73rd Amendment) Act, 1992 came into force to provide Constitutional status to the Panchayati Raj Institutions. This Act was extended to Panchayats in the tribal areas of eight States, namely Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Rajasthan from 24 December 1996. Now Panchayati Raj System exists in all the states except Nagaland, Meghalaya and Mizoram.
The Act aims to provide three-tier system of Panchayati Raj for all States having population of over 2 millicn, to hold Panchayat elections regularly every 5 years; to provide reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Women; to appoint State Finance Commission to make recommendations as regards the financial powers of the Panchayats; and to constitute District Planniug Committee to prepare draft development plan for the district. The three-tier system of Panchayati Raj consists of
a) village level panchayat
b) block level panchayat
c) district level panchayat.
Powers and Responsibilities are delegated to Panchayats at the appropriate level:
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
Being a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.








