Structure of Chromosomes

Structure of Chromosomes
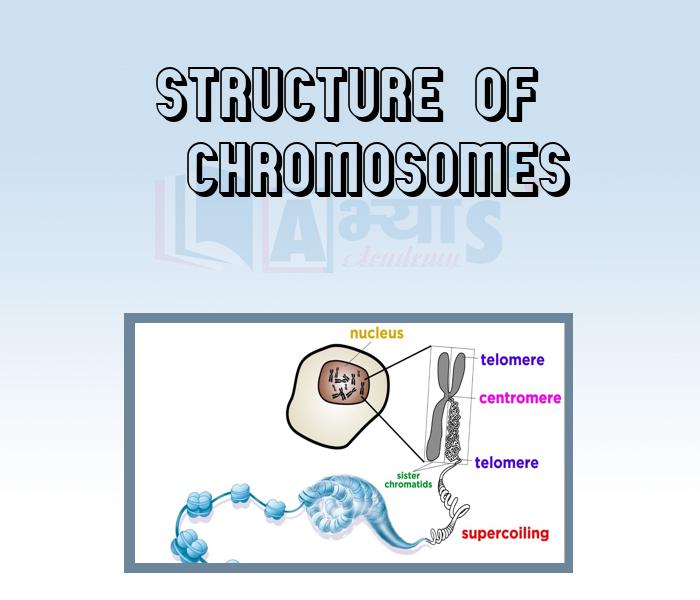
Chromosomes are thread - like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA). Chromosomes are passed from parents to offspring. The structure of a chromosome is consist of different parts. These parts are as follows :-
Centromere, Chromatids, Secondary constriction and satellite, Telomere, Chromomere, Chromonema and Matrix
A brief description of these parts are given below :-
Centromere
The region of chromosome with which spindle fibres are attached during metaphase is known as centromere or primary constriction or kinetochore. Centromere perform functions like orientation of chromosomes at metaphase, movement of chromosomes during anaphase, formation of chromatid and chromosome shape.
Chromatid
One of the two distinct longitudinal subuits of a chromosome is called chromatid. These subunits of a chromosome get separated during anaphase. Chromatids are of two types :- sister chromatids and non - sister chromatids.
Secondary constriction
The constriction or narrow region other than that of centromere is called secondary constriction. It has constant position and therefore can be used as useful marker. It is usually found in chromosome away from the centromere.
Telomere
The terminal region of a chromosome on either side is known as telomere. Each chromosome has two telomeres. The telomere of one chromosome cannot unite with the telomere of another chromosome.
Chromomeres
The linearly arranged bead like structures found on the chromosomes is known as chromomeres.
The linearly arranged bead like structures found on the chromosomes is known as chromomeres. These are clearly visible in the polytene chromosomes. Available evidences indicate that chromomere represents a unit of DNA replication, chromosome coiling, RNA synthesis and RNA processing.
Chromonema
Chromonema is a spirally coiled core of the chromosomes on which the genes are located. During the prophase of mitotic division, the chromosome material appears as thin filaments. These thin filaments are known as chromonema.
Matrix
Each chromosome is bounded by a membrane called pellicle. It is very thin and is formed of achromatic substance. This membrane encloses a jelly-like substance which is usually called matrix. In the matrix is present the chromonemata.

Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.
