Meristematic Tissue

Meristematic Tissue
PLANT TISSUES: Plant tissues are basically of two types : meristematic and permanent. This differentiation is based on the ability of the mature cells of the tissue to divide and produce new cells. Meristematic tissue cells are capable of dividing, while permanent tissue cells are not.
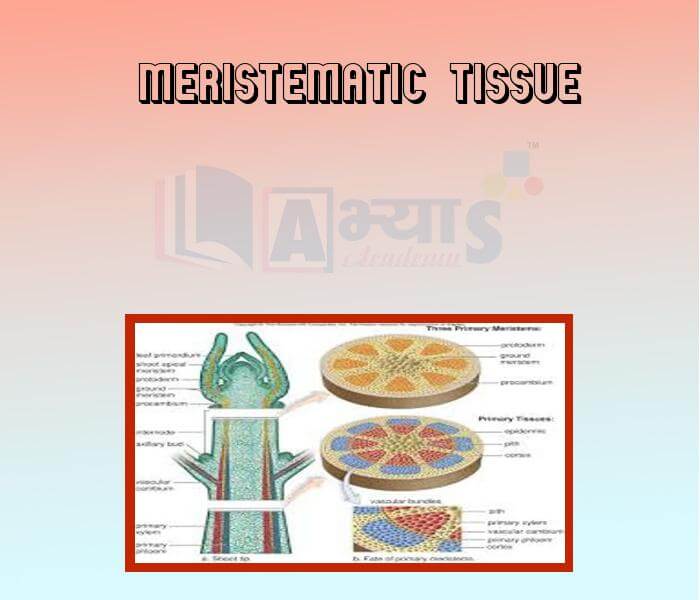
Meristematic Tissue: This tissue consists of actively dividing cells and is present in the growing regions of plants, e.g., the tips of roots and stems. The cells can be round, oval, polygonal or rectangular, but there are a few things they have in common. They are packed closely without intercellular spaces, have thin cellulose walls, dense cytoplasm and prominent nuclei. Vacuoles are almost absent in such cells because they are completely filled with sap.
There is more than one way of classifying meristematic tissue.
1. On the basis of origin, meristems (meristematic tissue) are of two types—primary and secondary. The former are derived directly from the meristems of the embryo. The latter develop later in the life of the plant from permanent tissues.
2. Based on the position in the plant or depending on the region of the plant where it is present, meristematic tissue can be of three types—apical, lateral and intercalary. In case of the roots due to the presence of root cap the growth of root occur sub apically. (I) Apical (from apex) meristem, as the name suggests, is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. Apical meristem is primary meristem. Cell division in this tissue causes elongation of the stem and root. Cells derived from the primary meristem differentiate into permanent tissues.
(II) Lateral meristematic tissue occurs along the sides of the central (longitudinal) axis of the plant. It gives rise to vascular tissues. Each year new vascular tissues are formed to transport food. These appear as rings. These rings of small and large vessels which are added on each year, cause growth in the thickness of the stem or trunk. Intrafascicular cambium present in vascular bundles and cork cambium found underneath the bark of trees are examples of lateral meristem. Lateral meristems are secondary meristems.
(III) Intercalary meristems occurs at the base of leaves or internodes. These cells grow fast and soon change into permanent tissues.

Lateral meristem is responsible for ______________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
In which of the following, growth is sub-apical ? | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Meristematic tissues responsible for increase in girth of plants are______. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.
