Joints And Movement











Joints And Movement
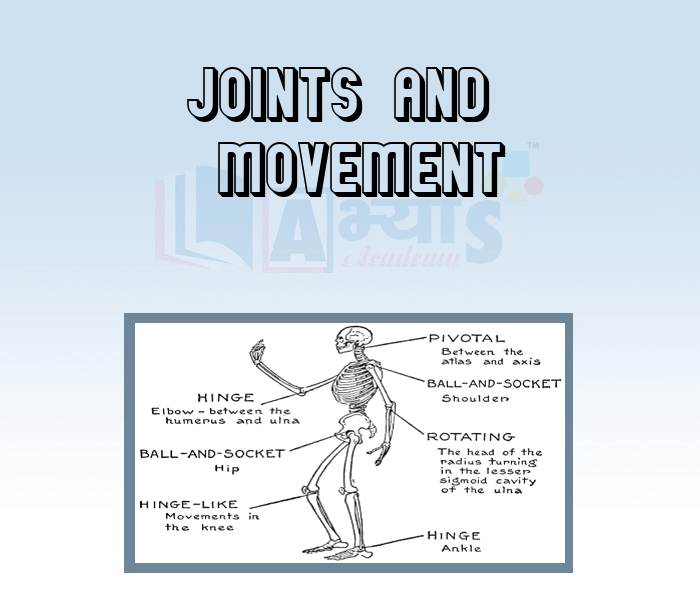
The joints in the body are the places where two bones are joined together. The joints are strong enough to withstand jerks. The ends of bones are covered with soft cartilage. It acts as a shock absorber and reduces friction between the bones. Cartilage is also present in some parts of the body that are not as hard as the bones, for example the upper part of the ear. The bones are held together at the joints by strong, stretchy bands called Ligaments. There are many joints in the body. The joints are of three types, depending on the types of movement they allow—immovable, slightly movable and freely movable.
The bones in the skull (except the lower jaw bone) do not allow any movement. The joints between the ribs and the breast bone allow only slight movement. Most of the joints in the human body are freely movable joints. These freely movable joints are of four main types, depending on the type of movement they allow.
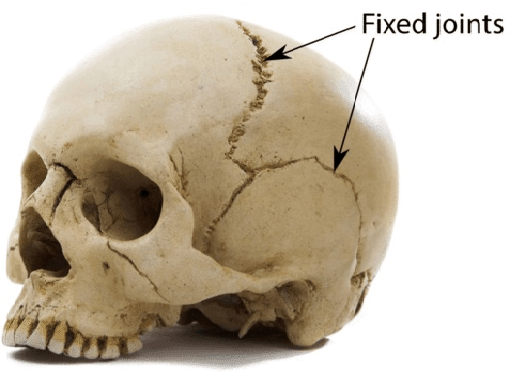
Immovable or fixed joints :
The joints do not allow any movement between the bones. For eg : the bone of skull are interlocked with each other and held together by fibrous cartilage, which do not allow any movement.
Slightly Movable joints:
These joints allow very little movement due to the presence of a pad of flexible cartilage between their ends. For example, joints present between adjacent vertebrae in the backbone or spine allow only slight movement. This kind of joint provides more support.
Freely movable joints :
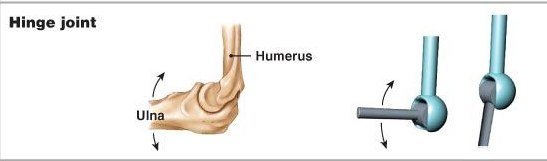
1. Hinge Joint:
The elbow, knee and finger joints allow movement in one plane only, that is, up and down, or backward and forward, like the hinges of a door. Such joints are therefore called hinge joints. We have hinge joints in our elbows, fingers, knees and toes.
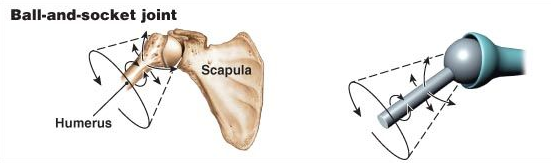
2. Ball and Socket Joint:
The shoulder and hip joints allow movement in all directions. In such joints, the end of one of the bones is round like a ball. It fits into a hollow part (or socket) in the other bone.
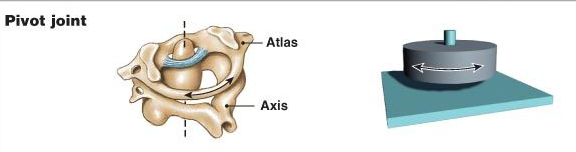
3. Pivot Joint:
The neck joint also allows movement in all directions. It allows you to move your head up and down, left and right and also to rotate it. In such joints, one of the bones ends in a rounded or conical surface that fits into a dent in the other bone. Such a joint is called a pivot joint.
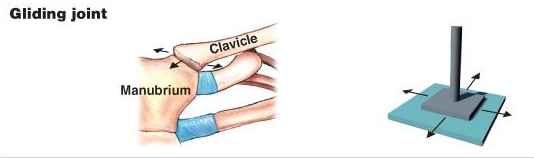
4. Gliding Joint:
The wrist or ankle joints have flattened ends of bones that can move ( or glide) against each other, These joints allow side to side as well as backward and forward movement. The vertebrae also have similar joints that allow slight movement. Gliding joints are found between the wrist and the carpals and between the ankle and the tarsals.
At which joint can the movement be only like the opening and closing of a door __________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The bones at joints are held together by ________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The type of joint in which a cylindrical bone rotates in a ring is which of the following types of joint? | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.
