Refraction of Light












Refraction of Light
When light traveling in a medium (such as air) enters another medium (such as water), it generally bends at the surface separating the two media. But once it is in the second medium, it moves along a straight line. This phenomenon of bending of light at the surface separating two media is commonly known as refraction of light.
The Change in the path of light ray as it passes from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light. If the refracted ray bends towards the normal we say that the Medium 2 is denser than Medium 1.But if the refracted ray bends away from the normal we say that the Medium 2 is rarer than Medium 1. The light ray that falls normally i.e. at right angles from medium 1 to medium 2 then it does not bend or change its path. Such a ray goes undeviated in medium 2.
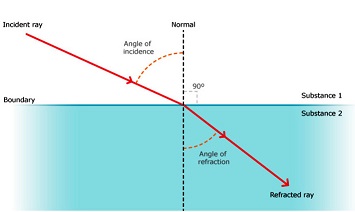
The surface separating the two media is also called the interface between them. Not the entire light incident on the interface between two media passes into the second medium after refraction; a small part of light gets reflected too.
Cause of Refraction:
Refraction of light takes place due to the change in the speed of light as it enters the medium 2 from medium 1.
Effects of Refraction in Our Day to Day life:
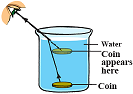
1. A spoon dipped in water. The part of the spoon in air and water appears to be disjoint.

2. While standing in a clear pool of water, the bottom looks raised and our legs appear shorter.

3. The bottom of a glass tumbler filled with water appears raised when viewed from above.
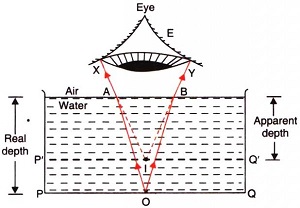
4. If we put pins or coins in a tumbler filled with water and look from the side, their images appear enlarged.
5. Our ability to see also depends on refraction. Our eyes contain several transparent liquids. When light from an object enters our eyes, it is refracted at the surfaces of these liquids to produce an image.
6. Refraction is also responsible for such wonderful things as the twinkling of stars and the sparkling of diamonds.
Illustration: If while standing on the bank of a stream you wished to catch a fish swimming in the water in front of you, would you aim above, below or directly at the observed fish to catch it?
Solution: As the fish is inside the water, so the rays coming are refracted at the surface of water. The fish will appear to be at a higher position. In order to catch the fish we will aim below the position observed.
Which of the following are correct ? (a) The change in the path of light ray as it passes from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light. (b) The light ray that falls normally at right angles from medium 1 to medium 2 then it does not bend or change its path. (c) The surface separating the two media is also called the interface between them. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
When white light is passed through prism, it splits into ______________- | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) This phenomenon of bending of light at the surface separating two media is commonly known as refraction of light . (b) Refraction of light takes place due to the change in the speed of light as it enters the medium 1 from medium 2. (c) An example of the effects of refraction in our day to day life is that the part of the spoon in air and water appears to be disjoint. | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.
