Respiration among Plants











Respiration among Plants
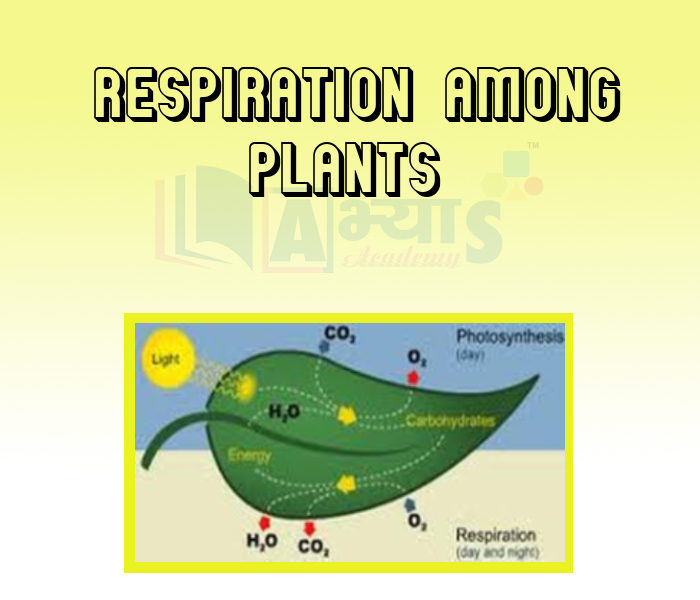
Respiration in Plants: Plants do not have any special organ to perform respiration. They exchange gases through stomata and large intercellular spaces present throughout the plant body ensure that all cells are in contact with air.
Root, stem and leaf are involved in this process.
1) Gaseous exchange in stem: In woody plants, gaseous exchange occurs through the small pores in the stem called ‘lenticles’. On the other hand, in herbaceous plants. Stomata on the stem aid in the respiratory process.
2) Gaseous exchange in leaves: In leaves, respiration takes place by diffusion of oxygen through stomata into the cells of the leaf. Stomata are the aerating pores present on the epidermis of the leaf. Each stomata pore is bordered by a pair of kidney shaped guard cells bearing chloroplasts in them. During daytime, when photosynthesis occurs, the carbon dioxide is rapidly used up, while the oxygen release is the major event. On the other hand, during night time, the elimination of carbon dioxide takes place.
.png)
3) Gaseous exchange in Roots: The root cells too require oxygen to produce energy. Roots have numerous tiny hairs on them. The soil has air trapped inside it. The oxygen (air) present in the soil diffuses into the root hair and is transported to the entire plant. The waste products formed in the form of water vapour and carbon dioxide are sent back to the surrounding through root hair by the process of diffusion. The soil of the potted plant is tilled so that air can reach to the soil at the bottom of the pot. If the plant is watered continuously, then the level of oxygen will decrease because too much of water will remove all the air present between the soil particles and the plant may die due to suffocation.
Which of the following are correct ? (a) Plants respire through tiny holes or openings called stomata. (b) Stomata trap air and exchange of gases takes place inside plant cell . Starch(sugar) + oxygen | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) Plants respire through tiny holes or openings called stomata. (b) Oxygen diffuses into the root hair and passes into the root cells from where the carbon dioxide moves out into the soil. (c) In woody plants, gaseous exchange occurs through the small pores in the stem called ‘lenticles | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) Exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in plants takes place through the tiny pores in the leaves known as stomata. (b) In woody plants, gaseous exchange occurs through the small pores in the stem called ‘lenticles’. | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
A marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
