Longitudinal and Transverse Waves










Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Types of waves: Mainly there are two types of waves.
Longitudinal Waves:
When the direction of wave motion in a medium is along or parallel to the direction of vibrating particles in the medium, such waves are called longitudinal waves. Longitudinal waves can be generated in all mediums. The individual particles of the medium move in a direction parallel to the direction of propagation of the disturbance. The particles do not move from one place to another but they simply oscillate back and forth about their positions of rest. This is exactly how a sound wave propagates, hence sound waves are longitudinal waves. Longitudinal waves can be produced in all the three media such as solids, liquids and gases.
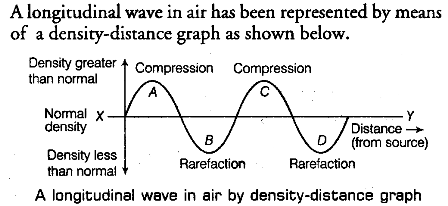
Graphical Representation of a Longitudinal Wave: When a longitudinal wave passes through air, the density of air changes continuously.
Transverse Waves:
When the direction of wave motion in a medium is perpendicular to the direction of vibrating particles in the medium, this type of waves are called transverse waves. Transverse waves can only be generated in the solid medium and on the upper surface of the fluid. Transverse waves cannot be produced within liquids and in gases. Transverse waves are transmitted as crest and trough. In transverse waves, the individual particles of the medium move about its mean position in a direction perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. e.g. Light is a.transverse wave (but it is not a mechanical wave). Transverse waves can be produced only in solids and liquids but not in gases. Examples:
1. The waves produced by moving one end of a long spring or rope, up and down rapidly, whose other end is fixed, are transverse waves.
Water waves are | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation |
Which of the following are correct : (a) Transverse waves can be produced only in solids and liquids but not in gases. (b) Longitudinal waves can be produced in all the three media such as solids, liquids and gases. (c) Transverse waves can be produced in all the three media such as solids, liquids and gases. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Sound travels in rocks in the form of ________________________ | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.
