Layers Of The Atmosphere










Layers Of The Atmosphere
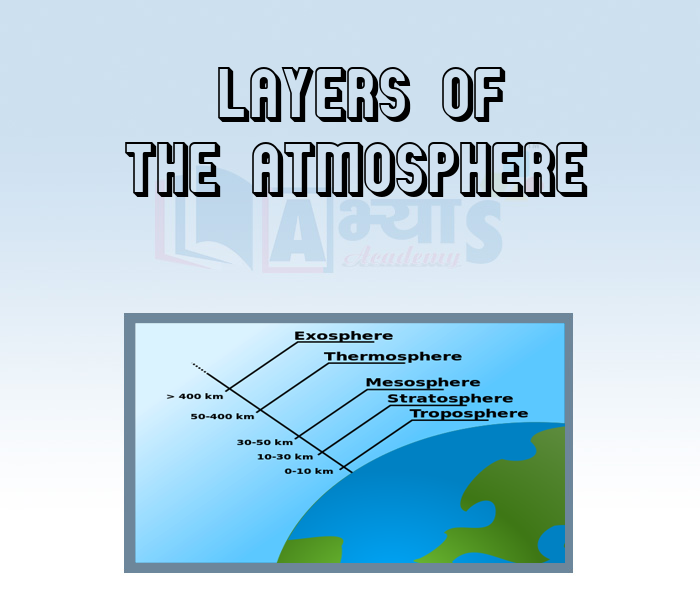
Layers Of The Atmosphere: Earth's atmosphere can be divided into five main layers. These layers are determined mainly by the fact that whether temperature increases or decreases with altitude. From highest to lowest, these layers are:
Exosphere: The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere extends from the exobase upwards. It is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium. The particles are so far apart that they can travel hundreds of kilometres without colliding with one another. Since the particles rarely collide, the atmosphere no longer behaves like a fluid. These free-moving particles follow ballistic trajectories and may migrate into and out of the magnetosphere or the solar wind.
Thermosphere: Temperature increases with height in the thermosphere from the mesopause up to the thermopause; then remains constant with height. The temperature of this layer can rise up to 1,500 °C (2,730 °F), though the gas molecules are so far apart that temperature in the usual sense is not well defined. The International Space Station orbits in this layer, between 320 and 380 km (200 and 240 mi). The top of the thermosphere is the bottom of the exosphere, called the exobase. Its height varies with solar activity and ranges from about 350-800 km (220-500 mi; 1,100,000-2,600,000 ft).
Mesosphere: The mesosphere extends from the stratopause to 8o-85 km (50-53 mi; 260,000-280,00o ft) upwards. It is the layer where most meteors burn up upon entering the atmosphere. Temperature decreases with height in the mesosphere. The top of the mesosphere is the coldest place on Earth and has an average temperature around -85 °C(-121 "F; 188.1 K). Due to the cold temperature of the mesosphere, water vapours get frozen, forming ice clouds (or Noctilucent clouds). A type of lightning referred to as either sprites or ELVES, form many miles above thunderclouds in the troposphere.
Stratosphere: The stratosphere extends from the tropopause to about 51 km (32 mi; 170,000 ft) upwards. Temperature increases with height, which restricts turbulence and mixing The stratopause, which is the boundary between the stratosphere and mesosphere, typically is at 50 to 55 km (31 to 34 mi; 160,000 to 180,000. The pressure here is 1/1,000 sea level,
Troposphere: The troposphere is the lowermost layer of the atmosphere. It is the most important layer because almost all of the weather phenomena (e.g. fog, cloud, dew, frost, rainfall, hailstorm etc.) occur in this layer. Temperature decreases with increase in height at the rate of 6.5" per 1,00o m. This rate of decrease in temperature is called normal lapse rate. There is seasonal variation in the height of troposphere In height changes from equator towards the poles (decreases) and from one season of a year to another season (increases during summer and decreases during winter), The average height of troposphere is about 16 km over the equator and 6 km over the poles. The upper limit of the troposphere is called tropopause, whích is about 1.5 km thick.
Other layers: Within these major layers of the atmosphere, there are some minor layers:
The ozonosphere is the lower portion of the stratosphere having maximum concentration of ozone. It is confined between the height of 15 km to 35 km from sea level. About 90% of the ozone in our atmosphere is contained in the stratosphere.The ionosphere extends from 80 km to 640 km. There are a number of ionic layers (with increasing heights) in this sphere, e.g. D layer, E layer, F layer, and G layer. The ionosphere radiates signals of various frequencies of radio waves to the earth's surface. It is also responsible for auroras. On the basis of chemical composition, the atmosphere is divided into two broad zones viz.
(i) homosphere,
(ii) heterosphere.
Homosphere is the lower portion of atmosphere lying up to the height of 90 km from the sea level. Troposphere, Stratosphere and Mesosphere form the parts of this layer.
Heterosphere extends from 90 km to 10,000 km. There are four distinct layers of gases in this sphere with molecular nitrogen in the lowest portion, followed by oxygen layer and helium layer. Hydrogen layer is found at its top.The average temperature of the atmosphere at the surface of the Earth is 14°C (57°F).
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
About Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.
