| e-NOTES (1614 [C] ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8th (Chemistry) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metals and Non Metals II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corrosion and its PreventionCorrosion:Iron and many other metals react with oxygen and moisture present in the atmosphere. This phenomenon is called corrosion. The process of slow eating away of a metal due to the attack of atmospheric gases and moisture on its surface is called corrosion. • Iron reacts with oxygen and moisture present in the atmosphere to form a brown, flaky substance called rust. Rusting of iron in an undesirable reaction because the layer of rust formed falls off, exposing the metal to further rusting. Prevention of rusting:Both air and water are needed together to rust the iron. The only way to prevent iron from rusting is to keep air and water away from it. It can be done by: Copper objects get coated with a green substance called basic copper carbonate with the passage of time. This green substance is formed due to the reaction of copper with carbon dioxide and moisture present in the atmosphere. Silver objects become blackened and lose their shine with the passage of time. This happens due to the reaction of silver with hydrogen sulphide gas present in the atmosphere. When a copper vessel is exposed to moist air for long, it acquires a dull green coating. The green material is a mixture of copper hydroxide The major problem of corrosion occurs with iron (or steel) as it is used as a structural material in industries like construction, infrastructure, bridges heavy industries etc. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metals React With AcidsMetals React with Acids:Metals: when a metal reacts with an acid, a salt and hydrogen gas are produced. Salt are compounds formed when a metal replaces hydrogen in an acid. Different acids and metals react to form different salts. Zinc reacts with sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas. Magnesium reacts with sulphuric acid to form magnesium sulphate and hydrogen gas. Aluminum reacts with hydrochloric acid to form aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. With some metals, the reaction is very fast and vigorous, while with others it may be slow. Some metals do not react with acids at all. Non-metals generally do not react with acids. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reactivity SeriesReactivity Series:The reactivity series of the metals, also known as the activity series, refers to the arrangement of metals in the descending order of the reactivities. The data provided by the reactivity series can be used to predict whether a metal can displace another an a single displacement reaction.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metals React With Other Metal SaltsDisplacement Reactions:In a displacement reaction, a metal reacts with a salt solution and ‘displaces’ (or replaces) the metal present in it. Displacement reactions are explained on the basis of the activity series of metals. The activity series of metals is a list of common metals arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity. This means that a metal which is placed higher in the activity series is more reactive than those placed below it. A metal will only react with a salt solution if it is placed higher in the activity series than the metal in the salt. For example, iron, which is placed higher in the activity series than copper, reacts with copper sulphate solution. Silver does not react with zinc sulphate. Zinc reacts with copper sulphate to form zinc sulphate and copper. Sliver does not react with copper sulphate. From the above reaction, we can conclude that the order of reactivity of zinc, copper, and silver is: Zn > Cu >Ag (i.e, Zinc is the most reactive of the three and silver, the least reactive). Aluminium and iron displace copper from solution of copper sulphate. Magnesium and zinc also displace copper from copper sulphate solution. Displacement reaction does not occur in the following cases. Here in the above reaction tin would be seen to displace lead from lead chloride. In the reaction below tin could not displace the iron as tin is less reactive than the iron.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uses of MetalsUses of Metals:Uses of some common metals are as follows. Metals like iron is used for making automobiles, machinery, pipes, containers, nails, etc. gold and silver are used for making jewellery. Copper:1. For making electrical wires and utensils. 2. For making coins and statues 3. For making boilers Aluminium:1. For king utensils 2. As foils used for wrapping chocolates etc 3. Mixed with other metals in the construction of aircraft. Iron:1. Pipes, storage tanks 2. Used in manufacture of nails, nuts and bolts etc. 3. Stainless steel is used for making utensils and surgical instruments. Zinc1. Mainly used as a protective coating for iron. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uses of Non MetalsUses of Non-metalsUsed to manufacture of matches. The head of safety matches are made of an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate, mixed with sulfur, fillers and glass powder. Hydrogen:1. Used for making fertilisers by ammonia 2. Liquid Hydrogen is used as fuel in spaceships Carbon:1. Diamond is used as a gem, and for cutting glass. 2. Graphite is used as a lubricant and used in pencils. Oxygen:1. By Human beings and animals for breathing 2. For generation of flames used in welding Phosphorus:1. Used in firework industry. Sulphur:1. Used to manufacture sulphuric acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alloys and its ImportanceAlloy An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals or one or more metals and a non- metal. Alloys can be used to increase hardness of metals. Examples of alloys are stainless steel (a mixture of iron, nickel, and chromium) and bronze (a mixture of iron and tin).
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metals React With WaterMetals React with Water:Metals react with water and produce a metal oxide and hydrogen gas. Metal oxides that are soluble in water dissolve in it to further form metal hydroxide. But all metals do not react with water. Metal + Water → Metal oxide + Hydrogen Metal oxide + Water → Metal hydroxide Metals like potassium and sodium react violently with cold water. In case of sodium and potassium, the reaction is so violent and exothermic that the evolved hydrogen immediately catches fire. 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy The reaction of calcium with water is less violent. The heat evolved is not sufficient for the hydrogen to catch fire. Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal. Magnesium does not react with cold water. It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen. It also starts floating due to the bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface. Metals like aluminium, iron and zinc do not react either with cold or hot water. But they react with steam to form the metal oxide and hydrogen. 2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g) 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g) Metals such as lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
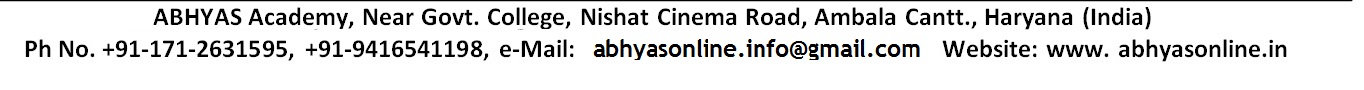 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Powered by ABHYAS ChatBOT.

What describes you best?

I am a Student
I am a Tutor
I am a School Owner
I want to appear for Govt. Exams